Concepts
-
Map: A map is a visual representation of an area that depicts the spatial distribution of features such as landscapes, urban infrastructure, or natural resources. Maps use symbols, colors, and scales to simplify and display real-world data.
-
Spatial Information: Spatial information refers to data about the location, shape, size, and relationships of physical objects or phenomena on Earth. It is often georeferenced, meaning it is tied to specific coordinates (latitude and longitude).
-
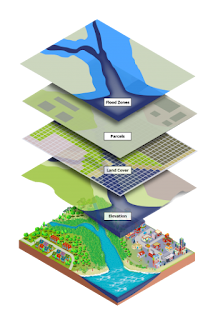
Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS is a framework that allows for the capture, storage, manipulation, analysis, and visualization of spatial information. It integrates maps with datasets to reveal patterns, relationships, and trends.
Key Terminologies
-
Coordinates: A system of numbers (e.g., latitude and longitude) used to define the exact location of a point on the Earth's surface.
- Example: 37.7749° N, 122.4194° W (San Francisco, USA).
-
Layers: In GIS, a layer represents a specific type of spatial information (e.g., roads, rivers, or population density), which can be overlaid on a map.
-
Attributes: Non-spatial data linked to spatial features. For example, a road feature may have attributes such as name, type, and width.
-
Thematic Maps: Maps focused on a specific theme, such as climate zones or crime rates.
-
Projections: Mathematical transformations that convert the Earth's 3D surface into a 2D map. Examples include Mercator projection and Lambert conformal conic projection.
-
Scale: The ratio of a distance on the map to the actual distance on the ground. For instance, a 1:50,000 scale means 1 unit on the map represents 50,000 units in reality.
Examples
-
Navigation Maps: Google Maps is a common example, displaying roads, buildings, and landmarks with turn-by-turn directions.
-
Thematic Analysis: A land use map showing areas of urbanization, agriculture, forest cover, and water bodies to understand human impact on the environment.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Using GIS, researchers can map forest fires to identify affected areas and proximity to communities.
-
Disaster Management: Flood risk maps integrate rainfall data, terrain elevation, and population density to guide evacuation planning.
Importance of Maps and Spatial Information
-
Urban Planning: Identifying optimal locations for infrastructure development (e.g., schools or hospitals).
-
Environmental Conservation: Tracking deforestation or monitoring wildlife habitats.
-
Agriculture: Mapping soil types and rainfall patterns to enhance crop yield predictions.
-
Disaster Response: Providing real-time data on hazards like earthquakes or hurricanes.
By combining maps with spatial information, we gain a powerful tool to analyze geographic data, solve complex problems, and visualize relationships that are otherwise hard to interpret. Tools like GIS elevate this process, enabling precise decision-making in diverse fields such as urban planning, disaster management, and environmental conservation.
Comments
Post a Comment