Disaster Management Act, 2005. National Disaster Management Framework (NDMF) National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA). National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM). National Disaster Response Force (NDRF)
Disaster Management Act, 2005.
National Disaster Management Framework (NDMF)
National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA). National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM).
National Disaster Response Force (NDRF)
The National Disaster Management Framework (NDMF) in India is a comprehensive policy document that provides a framework for managing disasters in the country. The framework was first introduced in 2005 and was updated in 2019.
The NDMF is based on the principle of an integrated approach to disaster management. It aims to bring together all stakeholders, including the government, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), civil society, and the private sector, to work towards a common goal of disaster management.
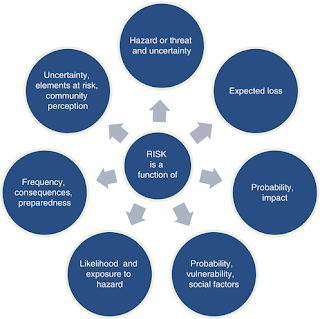
The framework is designed to address all phases of disaster management, including prevention, preparedness, response, and recovery. It provides guidelines for various aspects of disaster management, including risk assessment, disaster planning, early warning systems, search and rescue operations, relief and rehabilitation, and capacity building.
One of the key features of the NDMF is the creation of disaster management plans at various levels of government, including the national, state, and district levels. These plans are designed to address the specific needs and vulnerabilities of each area and to ensure that resources are allocated in a timely and effective manner.
The NDMF also emphasizes the importance of community participation in disaster management. It recognizes the crucial role that local communities can play in disaster preparedness and response and encourages the development of community-based disaster management plans.
In addition, the NDMF provides for the establishment of specialized institutions, such as the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), the National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM), and the National Disaster Response Force (NDRF), to help manage disasters in the country.
Overall, the National Disaster Management Framework in India is a comprehensive policy document that provides a roadmap for managing disasters in the country. It emphasizes an integrated approach to disaster management and encourages the participation of all stakeholders, including communities, in disaster preparedness, response, and recovery efforts.
..
Disaster Management Act, 2005.
The Disaster Management Act, 2005 is a legislation enacted by the Indian Parliament to provide for effective management of disasters in the country. The Act came into force on 23 December 2005 and replaced the earlier Disaster Management Act, 2003.
The key features of the Disaster Management Act, 2005 are as follows:
Establishment of National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA): The Act provides for the establishment of the NDMA as the apex body responsible for disaster management at the national level. The NDMA is headed by the Prime Minister of India and comprises of various experts and government officials.
Establishment of State Disaster Management Authority (SDMA): The Act provides for the establishment of the SDMA in every state as the apex body responsible for disaster management at the state level. The SDMA is headed by the Chief Minister of the state and comprises of various experts and government officials.
Preparation of Disaster Management Plans: The Act mandates the NDMA and SDMA to prepare and review disaster management plans for the country and every state, respectively. The plans must be reviewed and updated every five years or as and when required.
Formation of Disaster Response Force: The Act provides for the formation of the National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) and the State Disaster Response Force (SDRF) to assist in disaster management.
Provisions for Disaster Relief: The Act provides for the establishment of the National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF) and the State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF) for providing immediate relief to the affected people.
Measures for Prevention and Mitigation: The Act lays down provisions for prevention and mitigation of disasters. It mandates the NDMA and SDMA to take measures for identification, assessment, and mitigation of risks of disasters.
Coordination and Monitoring: The Act provides for the establishment of a coordination committee at every level for effective coordination and monitoring of disaster management activities.
Overall, the Disaster Management Act, 2005 provides a comprehensive legal framework for disaster management in India. It mandates various institutions and bodies to work together for effective management of disasters and lays down provisions for prevention, mitigation, and relief measures.
National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA).
The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) is an apex body established in India for disaster management. It was set up under the Disaster Management Act, 2005, which provides a legal framework for disaster management in the country.
The NDMA is responsible for laying down policies, plans, and guidelines for disaster management at the national level. It also coordinates the efforts of all agencies involved in disaster management and provides technical assistance and support to state governments and other stakeholders.
The NDMA is headed by the Prime Minister of India, who is the ex-officio chairperson of the authority. The members of the NDMA include senior government officials, experts in disaster management, and representatives from civil society organizations.
The key functions of the NDMA include:
Preparation of a national disaster management plan and guidelines for various stakeholders.
Capacity building and training of various stakeholders in disaster management.
Coordinating and monitoring the implementation of disaster management plans at the national, state, and district levels.
Providing technical assistance to state governments and other stakeholders in disaster management.
Undertaking research, studies, and documentation of best practices in disaster management.
Ensuring that disaster management plans are in place for various sectors, such as health, education, and agriculture.
Creating awareness among the general public about disaster management and promoting community participation in disaster preparedness and response.
Overall, the NDMA plays a crucial role in disaster management in India. It provides a framework for disaster management at the national level and ensures that various stakeholders work together to effectively manage disasters and minimize their impact on people, property, and the environment.
..
National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM)
The National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM) is a premier institution in India established to enhance the capacity of stakeholders involved in disaster management. It was set up under the Disaster Management Act, 2005, and is located in New Delhi.
The NIDM is responsible for promoting and undertaking research, training, and capacity building in the field of disaster management. It also provides technical assistance and support to state governments, NGOs, and other stakeholders involved in disaster management.
The key functions of the NIDM include:
Conducting research and studies in disaster management to develop best practices and policies.
Developing training modules and conducting training programs for various stakeholders involved in disaster management.
Providing technical assistance and support to state governments, NGOs, and other stakeholders in disaster management.
Creating awareness among the general public about disaster management and promoting community participation in disaster preparedness and response.
Collaborating with national and international institutions and organizations for knowledge sharing and capacity building.
Undertaking disaster risk reduction initiatives and developing disaster management plans for various sectors, such as health, education, and agriculture.
The NIDM has a state-of-the-art training infrastructure, including a virtual reality training centre, a disaster simulation laboratory, and an emergency operations centre. It conducts various training programs, workshops, and seminars for different stakeholders, including government officials, disaster management professionals, NGOs, and community leaders.
Overall, the NIDM plays a crucial role in enhancing the capacity of stakeholders involved in disaster management in India. It provides a platform for knowledge sharing, capacity building, and policy development in disaster management and promotes community participation in disaster preparedness and response..
..
National Disaster Response Force (NDRF).
The National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) is a specialized force established in India to provide quick and effective response to disasters. It was established under the Disaster Management Act, 2005, and is deployed for disaster response and relief operations across the country.
The NDRF is a multi-disciplinary force comprising of personnel from various fields, including engineering, paramedics, and communication experts. It is equipped with state-of-the-art equipment and technology to provide effective disaster response and relief operations.
The key functions of the NDRF include:
Search and Rescue Operations: The NDRF is trained in conducting search and rescue operations in various disaster scenarios, such as earthquakes, floods, and landslides.
Medical Support: The NDRF has a dedicated medical team that provides first aid and medical assistance to the affected people during disasters.
Communication Support: The NDRF has a communication team that provides communication support during disasters, including setting up communication networks and providing technical support.
Mitigation Measures: The NDRF provides technical support to state governments and other stakeholders in disaster management for identifying and implementing mitigation measures.
Capacity Building: The NDRF conducts training programs and capacity-building workshops for various stakeholders in disaster management.
International Cooperation: The NDRF works in close coordination with international organizations and other countries for knowledge sharing and capacity building in disaster management.
The NDRF is deployed for disaster response and relief operations across the country, and its teams are stationed in various locations across India for quick response. It has played a crucial role in various disasters, such as the Uttarakhand floods, the Chennai floods, and the Nepal earthquake.
Overall, the NDRF plays a crucial role in disaster management in India. It provides quick and effective response to disasters and supports state governments and other stakeholders in disaster management activities.
Comments
Post a Comment