Short-Wave Infrared (7, 6 4)

The short-wave infrared band combination uses SWIR-2 (7), SWIR-1 (6), and red (4). This composite displays vegetation in shades of green. While darker shades of green indicate denser vegetation, sparse vegetation has lighter shades. Urban areas are blue and soils have various shades of brown.
Agriculture (6, 5, 2)
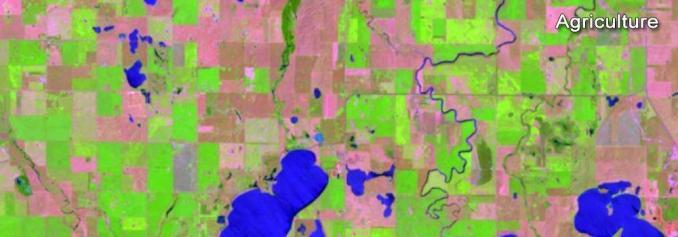
This band combination uses SWIR-1 (6), near-infrared (5), and blue (2). It's commonly used for crop monitoring because of the use of short-wave and near-infrared. Healthy vegetation appears dark green. But bare earth has a magenta hue.
Geology (7, 6, 2)

The geology band combination uses SWIR-2 (7), SWIR-1 (6), and blue (2). This band combination is particularly useful for identifying geological formations, lithology features, and faults.
Bathymetric (4, 3, 1)

The bathymetric band combination (4,3,1) uses the red (4), green (3), and coastal bands to peak into water. The coastal band is useful in coastal, bathymetric, and aerosol studies because it reflects blues and violets. This band combination is good for estimating suspended sediment in the water.
Natural Color (4, 3, 2)

The natural color composite uses a band combination of red (4), green (3), and blue (2). It replicates close to what our human eyes can see. While healthy vegetation is green, unhealthy flora is brown. Urban features appear white and grey and water is dark blue or black.
Color Infrared (5, 4, 3)

This band combination is also called the near-infrared (NIR) composite. It uses near-infrared (5), red (4), and green (3). Because chlorophyll reflects near-infrared light, this band composition is useful for analyzing vegetation. In particular, areas in red have better vegetation health. Dark areas are water and urban areas are white.
...
Comments
Post a Comment