Rayleigh scattering
Mie scattering
Nonselective scattering.
Interactions with the Atmosphere
Before radiation used for remote sensing reaches the Earth's surface it has to travel through some distance of the Earth's atmosphere. Particles and gases in the atmosphere can affect the incoming light and radiation. These effects are caused by the mechanisms of scattering and absorption.
Earth's atmosphere
Scattering occurs when particles or large gas molecules present in the atmosphere interact with and cause the electromagnetic radiation to be redirected from its original path. How much scattering takes place depends on several factors including the wavelength of the radiation, the abundance of particles or gases, and the distance the radiation travels through the atmosphere. There are three (3) types of scattering which take place.
Rayleigh scattering
Mie scattering
Nonselective scattering.
Rayleigh scattering occurs when particles are very small compared to the wavelength of the radiation. These could be particles such as small specks of dust or nitrogen and oxygen molecules. Rayleigh scattering causes shorter wavelengths of energy to be scattered much more than longer wavelengths. Rayleigh scattering is the dominant scattering mechanism in the upper atmosphere. The fact that the sky appears "blue" during the day is because of this phenomenon. As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, the shorter wavelengths (i.e. blue) of the visible spectrum are scattered more than the other (longer) visible wavelengths. At sunrise and sunset the light has to travel farther through the atmosphere than at midday and the scattering of the shorter wavelengths is more complete; this leaves a greater proportion of the longer wavelengths to penetrate the atmosphere.
Sunrise and Sunset
Mie scattering occurs when the particles are just about the same size as the wavelength of the radiation. Dust, pollen, smoke and water vapour are common causes of Mie scattering which tends to affect longer wavelengths than those affected by Rayleigh scattering. Mie scattering occurs mostly in the lower portions of the atmosphere where larger particles are more abundant, and dominates when cloud conditions are overcast.
Nonselective Scattering The final scattering mechanism of importance is called nonselective scattering. This occurs when the particles are much larger than the wavelength of the radiation. Water droplets and large dust particles can cause this type of scattering. Nonselective scattering gets its name from the fact that all wavelengths are scattered about equally. This type of scattering causes fog and clouds to appear white to our eyes because blue, green, and red light are all scattered in approximately equal quantities (blue+green+red light = white light).
AbsorptionAbsorption is the other main mechanism at work when electromagnetic radiation interacts with the atmosphere. In contrast to scattering, this phenomenon causes molecules in the atmosphere to absorb energy at various wavelengths. Ozone, carbon dioxide, and water vapour are the three main atmospheric constituents which absorb radiation.
Ozone serves to absorb the harmful (to most living things) ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Without this protective layer in the atmosphere our skin would burn when exposed to sunlight.
You may have heard carbon dioxide referred to as a greenhouse gas. This is because it tends to absorb radiation strongly in the far infrared portion of the spectrum - that area associated with thermal heating - which serves to trap this heat inside the atmosphere. Water vapour in the atmosphere absorbs much of the incoming longwave infrared and shortwave microwave radiation (between 22µm and 1m). The presence of water vapour in the lower atmosphere varies greatly from location to location and at different times of the year. For example, the air mass above a desert would have very little water vapour to absorb energy, while the tropics would have high concentrations of water vapour (i.e. high humidity).
Wavelengths that we can use most effectively
Because these gases absorb electromagnetic energy in very specific regions of the spectrum, they influence where (in the spectrum) we can "look" for remote sensing purposes. Those areas of the spectrum which are not severely influenced by atmospheric absorption and thus, are useful to remote sensors, are called atmospheric windows. By comparing the characteristics of the two most common energy/radiation sources (the sun and the earth) with the atmospheric windows available to us, we can define those wavelengths that we can use most effectively for remote sensing. The visible portion of the spectrum, to which our eyes are most sensitive, corresponds to both an atmospheric window and the peak energy level of the sun. Note also that heat energy emitted by the Earth corresponds to a window around 10 µm in the thermal IR portion of the spectrum, while the large window at wavelengths beyond 1 mm is associated with the microwave region.
Now that we understand how electromagnetic energy makes its journey from its source to the surface (and it is a difficult journey, as you can see) we will next examine what happens to that radiation when it does arrive at the Earth's surface.


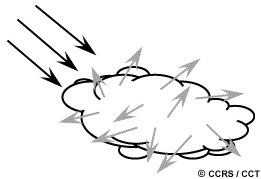


Mie scattering or non-molecular scattering or aerosol particle scattering.
ReplyDeleteMie scattering, also known as non-molecular scattering or aerosol particle scattering, is a type of scattering that occurs when electromagnetic radiation (such as light) interacts with particles that are much larger than the wavelength of the radiation. This type of scattering is characterized by a relatively broad angular distribution of the scattered radiation, and is caused by the interference of the scattered waves from different parts of the particle. Mie scattering is commonly observed in atmospheric physics and meteorology, where it plays an important role in the scattering of sunlight by aerosol particles such as dust, smoke, and water droplets. It is also used in a variety of other fields such as optics and materials science.
Mie scattering is important in remote sensing because it affects the way that electromagnetic radiation is scattered by particles in the atmosphere, which can have a significant impact on the measurement of atmospheric properties using remote sensing techniques. In particular, Mie scattering can cause a decrease in the amount of radiation that reaches a remote sensing instrument, which can make it more difficult to detect and measure certain atmospheric properties.
Mie scattering also changes the angular distribution of the scattered radiation, which can affect the directional characteristics of the radiation that reaches a remote sensing instrument. This can make it more difficult to determine the location and properties of atmospheric particles using remote sensing techniques.
However, remote sensing instruments can take advantage of Mie scattering properties to infer properties of the atmospheric particles such as size, shape, and refractive index. Remote sensing instruments such as lidar, radar, and radiometer can use Mie scattering to infer the size distribution and concentration of aerosol particles in the atmosphere, which are important for studying climate change, air quality and visibility.
In summary, Mie scattering can be a challenge for remote sensing but also a powerful tool to infer properties of the atmospheric particles.